Time of Flight Diffraction (TOFD) is one of the most sensitive and most accurate techniques for non-destructive examination of welded joints. Usage of TOFD allows for a very precise dimensioning of length and depth of cracks and other internal discontinuities. Unlike other ultrasonic techniques TOFD is not susceptible to an inconvenient orientation of the defect. Instead ultrasonic signal amplitude TOFD uses signals from diffraction waves to ascertain the location of the indications.
HOW DOES THE TOFD TECHNIQUE WORK?
TOFD uses a pair of heads located on opposite sides of the weld. One of the heads emits an ultrasonic signal that is captured by the other head. If there are no defects in the weld, two waves are received: one wanders just below the surface, the other one is reflected from the opposite surface (bottom). The ultrasound waveform diffraction pattern is detected by the receiver. Studies show that the TOFD technique is more reliable than x-ray.
Insensitivity to discontinuity orientation makes this technique highly repeatable and reproducible, which is widely used for monitoring discontinuities.
High data acquisition speed (up to 500 mm/s) results in significant increase of productivity and reduction of costs when testing long joints.
The TOFD technique is fully described by the applicable European standards. The acceptance criteria and testing levels are correlated with the quality levels in accordance with PN-EN ISO 5817 by the PN-EN ISO 17635, which means that the use of this technique, despite high detection, does not necessarily imply an increase in the number of joints to be repaired.
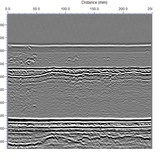
Application
The TOFD technique is only used for non-carbon steel butt joints, other materials always require sensitivity validation. It is problematic or not possible to test welded joints made of "stainless steel".
The standards allow testing joints from thickness of 6 mm; however, there are guidelines that increase this lower limit of TOFD use.

Important to know
Limited detection in the subsurface zones, especially the face, but also the root, can be solved with the use of additional probes (conventional or Phased Array).
Despite its limitations, it is one of the most sensitive NDT methods.
